Data Access Committee (DAC) Guide
DUOS Overview for DACs
How DUOS is Helping Data Access Committees (DACs)
DACs must answer important questions about access to data but often have to interpret complex and ambiguous inputs to those decisions
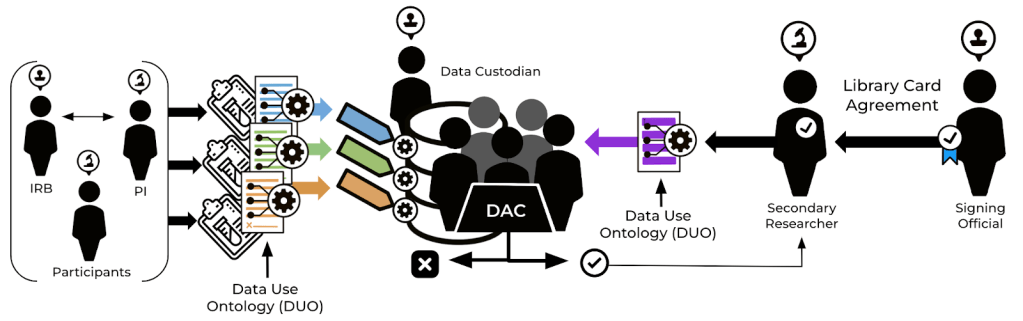
Currently, when DACs receive data access requests, they must decide if the proposed research use is within the bounds of the data’s use limitations dictated by its consent forms.
Unfortunately, data use limitations are often described with unique language across the various consent forms in which they appear (diagram left). Thus a DAC is left to either attempt to interpret the consent form or receive the original IRB’s interpretation (ex. NIH Institutional Certification, Broad Data Use Letter) to determine the official use limitations.
On the other hand (diagram right), researchers’ data access requests are often narrative scientific proposals of varying levels of depth and specificity.
The inconsistency and lack of clarity in the terms used to describe data use limitations and research proposals make it difficult for DACs to answer the question of “Is the proposed research within the bounds of the data use limitations?”
To resolve this issue, the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health created a common vocabulary for data use limitations and proposed research, called the Data Use Ontology (DUO; Lawson et al., 2021). The ontology is not only a standardized series of terms and definitions describing data use but is also computer-readable.
DUOS leverages the Data Use Ontology by enabling Data Submitters to describe their data use limitations with DUO terms, and Researchers to describe their research purposes with DUO terms. The result is that DACs using DUOS can compare data use limitations and research purposes using the same vocabulary of terms.
Additionally, with the use limitations and proposed research in DUO terms, DUOS can enable an algorithm to compute the comparison of the data use limitations and proposed research in an attempt to replicate the decision the DAC would make. Through testing, the DUOS algorithm has seen >90% agreement with DACs (Cabili et al., 2021). Currently, DACs are able to leverage the algorithm as a decision-support tool, reviewing the DUOS algorithm’s suggested decision prior to logging their own decision (Rahimzadeh et al., 2022). If the DUOS algorithm proves to consistently decide as the DAC would, DACs may choose to use the DUOS algorithm to automatically respond to data access requests.
DAC FAQs
Can my DAC use DUOS?
Yes! If you and/or your DAC are interested in using DUOS, please reach out to us at support@duos.org.
If my DAC wants to use DUOS, does my data have to be in a specific system?
Nope! Any dataset may be registered in DUOS, regardless of the physical location of the data. Data Submitters and DACs interested in using DUOS are responsible for making sure researchers approved for access via DUOS are able to access the data once approved. This process is streamlined for datasets ingested or indexed in the Terra Data Repository (TDR), a platform designed for storing and managing access to life sciences data. Learn more about DUOS’ integration with TDR by reading Streamlining Data Access.
How do I determine the data use limitations for my dataset(s)?
Our experienced and expert team is glad to consult with anyone needing guidance in assigning data use limitations to their datasets, which will ultimately need to be approved/accepted by the DAC agreeing to manage your datasets in DUOS.
Does DUOS store genetic data?
No. DUOS only stores the metadata you see displayed in the DUOS Data Library and curated data libraries in DUOS. All genetic data that may be requested via DUOS is stored in external systems, and predominantly in Broad’s Terra service, though the use of Terra is not required for DACs to register their data in DUOS.
If I make my data available via DUOS, does it need to be stored in a single location?
No. However, the Data Custodian for your dataset(s) will be responsible for providing access to researchers approved by the DAC, and having data in multiple locations will be increasingly complex for Data Custodians to set and maintain access permissions, and for researchers to access and analyze the data in aggregate. Storing or indexing data in the Terra Data Repository (TDR) further streamlines the access-management process. Read Streamlining Data Access to learn more about DUOS’ integration with TDR.
Can DUOS allow for multiple parties to review and approve a data access request?
Yes. There are two ways to enable multiple individuals to review a DAR in DUOS.
One option is to add multiple individuals to your DAC, as DAC Members. DAC Members are able to offer comments and a suggested vote to the DAC Chair, without directly controlling the final vote on the DAR. This option is most helpful for individuals who are in the same organization or consortium, or collaborate with one another.
Another option is to add multiple individuals to your DAC, as DAC Chairs. DAC chairs act autonomously, where any DAC Chair is able to deny or approve DARs, ultimately denying or granting access to data. This option is most helpful for DACs with policies that allow for varied decision-makers for DARs – often depending on DAR contents – examples of these roles may include Vice-Chairs or Deputies, or Coordinators.
Does DUOS automate data access requests?
DUOS offers DACs the option to automate data access requests for broadly consented datasets, when reserachers’ requests are straightforward, without ethical concerns. DACs can learn more about this feature by going to their DAC profile page, or by contacting support@duos.org.
